Menopause is a natural phase in a woman’s life when her menstrual cycles end. It typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 55, with the average age being around 51.
Menopause marks the end of a woman’s reproductive years, brought on by the decrease in hormone production, particularly estrogen and progesterone. While it is a normal biological process, the experience can vary significantly from person to person.
Understanding menopause is important because it affects both physical and mental health. For example, many women at different stages of menopause may experience hot flashes, mood changes, and sleep disturbances. So, having a good understanding of menopause and how to handle it is important to a woman’s state of mind and body.
You may wonder, “How many stages of menopause are there?” and “What stage of menopause am I in?” We will answer all your questions, including helping you know the stages of the menopause you’re in.
Understanding menopause and its different stages can help you better manage menopause symptoms and prepare for the transitions. You’ll also be able to make informed decisions about your health.
The Stages of Menopause
Menopause occurs in three stages: perimenopause, menopause, and postmenopause. These stages bring with them different changes to a woman’s body as hormone levels shift.
3. Perimenopause
Perimenopause is the first of the 3 stages of menopause, and it usually starts a few years before menopause. During this time, hormone levels, especially estrogen, begin to fluctuate. This can cause symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, and irregular periods. Women may also experience mood swings and difficulty sleeping during the stages of perimenopause.
Managing perimenopause symptoms can involve lifestyle adjustments like eating a balanced diet and staying physically active. Reducing stress through relaxation techniques and consulting with a healthcare provider can also help ease symptoms during this stage.
2. Menopause
Menopause is diagnosed when a woman has gone 12 months without a menstrual period. It marks the end of menstruation and the reproductive years. Some of the most common stages of menopause symptoms during this time include vaginal dryness, mood changes, and sleep disturbances. These symptoms can vary in intensity from person to person.
To support menopausal health during this stage, it’s helpful to maintain a healthy diet, stay active, and consider talking to a doctor about treatments, like hormone therapy or non-hormonal options. These lifestyle changes can promote better health as the body adjusts to the hormone changes.
3. Postmenopause
Postmenopause is the stage after menopause that lasts for the rest of a woman’s life. Although the symptoms experienced during menopause may lessen, this stage comes with its own long-term health considerations, such as a higher risk of osteoporosis and heart disease. Regular weight-bearing exercises and a nutritious diet rich in calcium and vitamin D can support bone health and reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
It is important to stay in touch with a healthcare provider during postmenopause to monitor and manage any long-term effects. While this stage marks the final phase of the stages of menopause, ongoing care is essential for maintaining health.
Perimenopause vs Menopause vs Postmenopause
Understanding the differences between perimenopause, menopause, and postmenopause is essential to recognize the unique challenges and experiences each stage brings.
Below is a table summarizing the key differences across the stages of menopause.
| Stage | When It Occurs | Key Characteristics | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Perimenopause | Typically begins in a woman’s 40s but can start earlier. | Hormonal fluctuations, mainly estrogen decline. | Hot flashes, night sweats, irregular periods, mood swings, difficulty sleeping, weight changes. |
| Menopause | Diagnosed after 12 months without a menstrual period. | Permanent cessation of menstruation. | Vaginal dryness, mood changes, sleep disturbances, reduced libido, weight gain. |
| Postmenopause | Begins after menopause and continues for the rest of a woman’s life. | Hormone levels stabilize at a lower level. | Risk of osteoporosis, heart disease; symptoms from menopause may ease but long-term health concerns increase. |
This stages of menopause chart highlights the differences between the three stages, making it easier to understand how they progress and affect the body.
Common Menopause Symptoms and Treatments
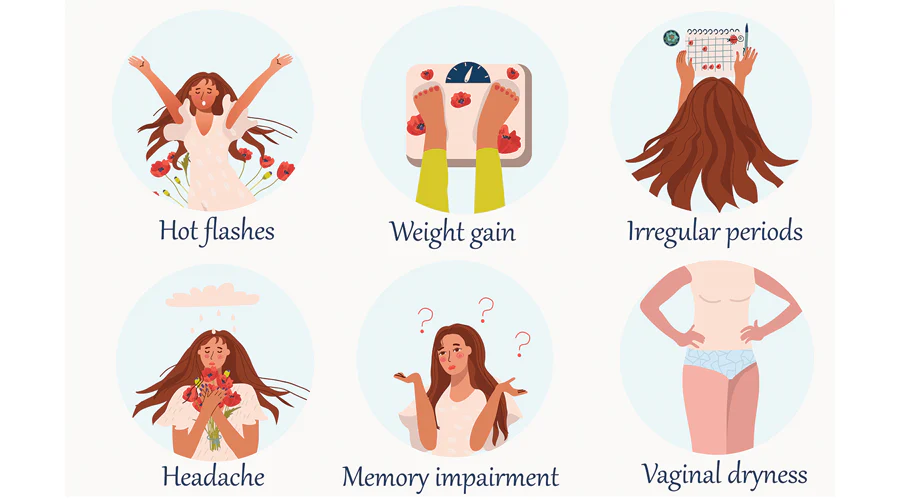 Menopause symptoms
Menopause symptomsAs women go through the different stages of the menopause, they experience a variety of symptoms. These can be both physical and emotional. Here are some of these symptoms and ways to manage them effectively:
Physical Symptoms
- Hot flashes and night sweats: These are among the most common symptoms during perimenopause and menopause. Hot flashes cause a sudden sensation of heat, often accompanied by sweating, flushing of the skin, and discomfort. They can occur at any time, disrupting daily activities or even sleep, which is why night sweats are particularly bothersome for many women.
- Vaginal dryness and discomfort: As estrogen levels drop, the vaginal walls thin and produce less natural lubrication, leading to dryness and discomfort during intercourse or regular activities. This symptom often emerges during menopause and can continue into postmenopause, affecting sexual health and well-being.
- Sleep disturbances: Difficulty sleeping is another common symptom. It can be linked to night sweats, anxiety, or general hormonal shifts, leading to feelings of fatigue during the day. Women may wake up frequently during the night or have trouble falling asleep.
For women experiencing sleep disturbances due to menopause, incorporating lifestyle changes and natural remedies can make a significant difference. For more helpful advice, check out Tips for Improving Sleep During Menopause to regain restful nights and reduce fatigue.
Emotional Symptoms
- Mood swings and irritability: Hormonal fluctuations can lead to sudden and intense changes in mood. Women might feel fine one moment and then become irritated or emotional the next. This emotional instability can be particularly difficult to manage without understanding its root cause.
- Anxiety and depression: For some women, the hormonal changes during the 3 stages of menopause may lead to feelings of anxiety, sadness, or depression. This can be compounded by the physical changes happening in the body, contributing to stress or a sense of uncertainty about the future.
Treatment Options
- Hormone therapy: This involves using estrogen or a combination of estrogen and progesterone to help manage symptoms like hot flashes and vaginal dryness. It’s most effective during perimenopause and menopause but may also help in postmenopause.
- Non-hormonal treatments: Many women prefer to manage their symptoms through lifestyle adjustments rather than hormone therapy. This can include regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, and stress-reducing activities like yoga or meditation. Supplements, such as calcium for bone health and plant-based remedies, may also provide relief from some symptoms.
- Complementary and alternative therapies: Some women explore natural or holistic treatments to manage the effects of menopause. Acupuncture, herbal remedies, and mindfulness practices are often used to manage hot flashes, mood changes, and other symptoms. It’s important to discuss these options with a healthcare provider to ensure they are safe and effective for individual needs.
Conclusion
Menopause is a significant phase in every woman’s life, and understanding the stages of the menopause—from perimenopause to postmenopause—is essential for effectively managing the changes that come with it.
Each menopause stage presents different symptoms and challenges, from hot flashes and night sweats during perimenopause to the health risks associated with postmenopause, such as osteoporosis and heart disease. Being aware of these shifts can help women prepare for and cope with the physical and emotional effects of menopause.
Self-care plays a crucial role in navigating the 3 stages of menopause. This can include maintaining a healthy diet, staying physically active, and finding ways to reduce stress. It’s equally important to seek support from healthcare providers, friends, or support groups to ensure that the journey through menopause is as smooth as possible.
By staying informed and proactive, women can better manage symptoms and maintain their overall health and well-being throughout this natural transition.

